Setting-up your environment
Section outline
-
REQUIREMENTS:
You will need to have a command line / terminal program running on your computer, it will be used for the practicals. Depending on your Operating System (OS), it will be more or less simple. Simple for Linux or Mac users.
Windows users, read below and let us know in advance if you fail installing a terminal program.
Mac OS X & Linux: a command line program is available by default, but if you have never used it before, locate it (Terminal.app with Mac) and start it.
Windows 10: Install a command line program.
1) Turn ON the "optional features" in the Control Panel. Shortcut: press Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog, type “optionalfeatures”, and press Enter. The list of available Windows features appears. If a feature has a checkmark next to it, it’s enabled. If a feature doesn’t have a checkmark, it’s disabled. Enable the “Windows Subsystem for Linux” option in the list, and then click the “OK” button.
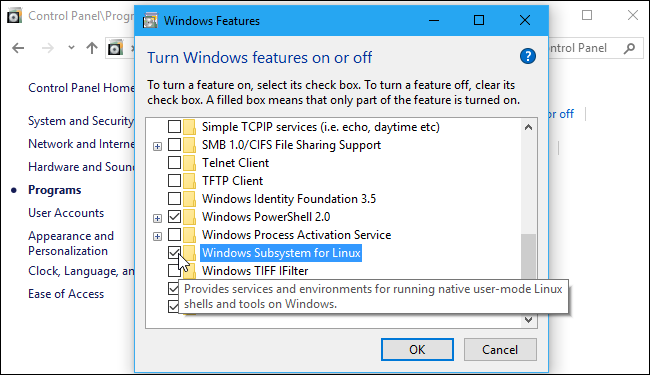
2) Restart your computer.
3) In Microsoft Store (you need an account), type Ubuntu (or another one if you know) and install it. More information available here: https://ubuntu.com/tutorials/ubuntu-on-windows#1-overview
After install, open Ubuntu. To get to your usual Documents folder, type cd /mnt/c/Users/yourUsername/Documents (replace "youUsername" with you user name).
Alternatively, instead of installing Ubuntu, you can downlad a Virtual Machine (VM image) Ubuntu detailed at the end of this section.
Older Windows OS: terminal program installation
We recommend you to install Mobaxterm, which provides all the important remote network tools (SSH, X11, RDP, VNC, FTP, MOSH, ...) and Unix commands (bash, ls, cat, sed, grep, awk, rsync, ...) to Windows desktop, in a single portable exe file which works out of the box. Download link to the free Home Edition: https://mobaxterm.mobatek.net/download.html
